restraints module¶
Ancillary restraints (B-factor, stereochemistry).
Module author: Michael S. Chapman <chapmanms@missouri.edu>
Module author: Leo Selker
Module author: Davis M. Catolico
- Authors:
Michael S. Chapman <chapmanms@missouri.edu>
Oregon Health & Science University & University of Missouri
- Version:
1, Nov 15, 2025
Changed in version 0.1.1: 08/29/11 Start
Changed in version 0.5.0: (5/2/15) ReStructured Text documentation
Changed in version 0.5.6: (10/21/15) Adding vdW restraint from Leo
Changed in version 0.5.7: (05/01/17) Starting covalent geometry restraints: bond lengths
Changed in version 0.5.8: (07/11/17) Distance (x-linking) restraints
Changed in version 0.5.9: (11/21/17) restraints: bond angle
Changed in version 1.0.0: (09/27/20) Python 2.7 –> 3.6 cmd2: optparse –> argparse: changed calls and decorators
See also
Limit() in torsion.py.
- class restraints.AminoAcid¶
Bases:
GeometrySuperclass definition of amino acid stereochemistry.
Engh R A & Huber R (1991). Acta Cryst., A47, 392-400
Subclasses Ala, Gly etc. define variations specific to the type of amino acid. Dictionary look up, keyed on tuples of the atoms defining the geometry. Values are tuples of (ideal value, estimated error). Key tuple should be defined in forward and reverse for bonds that are “symmetric” the exceptions being between different residues, i.e. Gly:C-N:Pro will be different from Pro:C-N:Gly.
Warning
Stereochemical definitions are incomplete in this class and subclasses. To be added to, with most essential geometries, but might never be complete, on the understanding that programs will restrain to starting values if ideal values are not available.
Warning
Dictionary values have been checked by running lengthDeviants(threshold=0.0) and angleDeviants(threshold=0.0) systematically for all bond different lengths, and spot-checking ~30 angles, comparing them to the orignal tables in Engh & Huber. This is not comprehensive, so users should be looking out for large deviants, in case these have resulted from inappropriate ideal values.
- types = ['Ala', 'Arg', 'Asn', 'Asp', 'Cys', 'Gln', 'Glu', 'Gly', 'His', 'Ile', 'Leu', 'Lys', 'Met', 'Phe', 'Pro', 'Ser', 'Thr', 'Trp', 'Tyr', 'Val']¶
- class restraints.Anchor(target, weight=1, selection=None)¶
Bases:
objectRestraint on displacement of selected atoms.
Deprecated since version 0.5.0: will replace with
- Parameters:
target (Atoms) – coordinates to which selected atoms in a paired coordinate set will be tethered.
weight (float) – multiplier for the anchor restraint.
selection (Selection|NoneType) – default anchor atoms in target
- check(atoms, selection=None)¶
Assert that atoms correspond to those in target
- Parameters:
atoms (Atoms) – current coordinates
selection (Selection|NoneType) – anchor atoms in target
- end_atoms = 3¶
Number of atoms to anchor (by default) at the ends of an internal segment of chain.
- stats(atoms, selection=None, verbose=False, check=True)¶
Printed statistics
- Parameters:
atoms (Atoms) – current coordinates
selection (Selection|NoneType) – anchor atoms in target
check (bool) – assert that selected atoms correspond to target
- class restraints.Arguments(imports=[], main=None, *args, **kwargs)¶
Bases:
ArgumentsManager for command-line arguments from main and imported modules.
This is a template to be copied into modules, for the handling of command- line options.
methods export() and domestic() should be overridden by the module subclass with declarations of the command-line arguments needed by the module.
- Parameters:
imports ((list of) ArgumentParser(s)) – (list of) module(s) from which to obtain “parent” ArgumentParser objects for inclusion.
main (bool|NoneType) – Add information and arguments appropriate for a main program (or not); if None, will determine by whether this class is defined in __main__.
- domestic()¶
Defines options used only when main program and not when imported.
- export()¶
Defines options used in both stand-alone and imported modes.
- class restraints.Brestraint(atoms, weight, group_exclusions=None)¶
Bases:
objectRestraint on variation of adjacent atomic displacement parameters.
- Parameters:
atoms (
Atoms) – atomic parameters (coordinates etc).weight (float) – empirical (user-adjusted) weight for the restraint.
group_exclusions (class
Group, bool or NoneType) – intra-selection restraints are excluded within this Group of (rigid) Selections.
- df(b)¶
Atomic partial derivatives for B-factor variation restraint.
- Parameters:
b (ndarray(type = float)) – current atomic displacement parameters (must be aligned w/ self._atoms.bonded)
- Returns:
weight * ∂Σj [Bi - Bj]2/∂Bj, for all j neighbors of i atoms
- Return type:
ndarray(type = float)
- f(b)¶
Objective function for B-factor variation restraint.
- Parameters:
b (ndarray(type = float)) – current atomic displacement parameters (b must be aligned with self._atoms.bonded)
- Returns:
Σi, j [Bi - Bj]2 * weight, for all j neighbors of i atoms
- Return type:
float
- rms(b)¶
RMS variation in B-factor for bonded atoms.
- Parameters:
b (ndarray(type = float)) – current atomic displacement parameters (b must be aligned with self._atoms.bonded)
- Returns:
(Σi, j [Bi - Bj]2)0.5, for all j neighbors of i atoms
- Return type:
float
- class restraints.ClassHolder¶
Bases:
objectSupports referencing a class using a string.
- add_class(cls)¶
Add a class
- Parameters:
cls (class)
- class restraints.Commands(tasks=None, initial_commands=None, py_locals={}, parser=None)¶
Bases:
objectOptimization cmd2 commands for importing/subclassing to other modules.
Todo
This should be a sub-class of TopCmd with the commented-out super().__init__, but would need to get the tasks object through here, so giving up for now, 11/25/20.
- ap1 = ArgumentParser(prog='sphinx-build', usage=None, description=None, formatter_class=<class 'argparse.HelpFormatter'>, conflict_handler='error', add_help=True)¶
- do_restraints(args)¶
Input (and statistics) for supplementary restraints.
- class restraints.CovalentRestraint(start, weight=1, parameterization=None, ideal=None, wtLength=1.0, wtAngle=1.0, verbose=True)¶
Bases:
objectRestraint on covalent bonding.
Implemented for efficiency in torsional or rigid group refinements that are mostly constrained covalently, and where sparse restraints are needed just for the geometry between segments.
Warning
Statistics are calculated only between segments, not all-atom, and are therefore not appropriate for quality evaluation, just for monitoring progress of a refinement.
List atoms and target values for geometries to be restrained.
Distances, .. todo:: Angles and Dihedrals
- Parameters:
start (Atoms) – coordinates used to (a) determine connectivity; for restraint to starting geometry if ideal targets unavailable.
weight (float) – multiplier for the covalent bond residual restraint, see also wtLength and other weights for individual terms.
parameterization (:py:class:'AtomicParameterization' or sub-class) – definition of what parameters are refining and how they depend on atomic parameters. This is used here to limit stereochemical restraints to bonds between torsional or rigid segments.
ideal (Dictionary) – definitions of ideal geometries
wtLength (float) – multiplier for the bond length term, noting that terms for each bond are additionally inverse-variance weighted, and that the overall stereochemistry weight is also applied.
wtAngle (float) – multiplier for the bond angle term, noting that terms for each bond are additionally inverse-variance weighted, and that the overall stereochemistry weight is also applied.
- angle¶
- Variables:
~.length (list(tuple)) – i_atom_A, i_atom_B, target, sigma
~.angle (list(tuple)) – i_atom_A, i_atom_B, i_atom_C, target, sigma
- angleDeviants(atoms, threshold=0.0)¶
Deviations from ideal of covalent bond angles above threshold*esd.
- Parameters:
atoms (Atoms) – current (trial) coordinates
threshold (float) – eg. 3.0 to print deviations >= 3 sigma.
- Returns:
Table of greatest deviations
- Return type:
str
- angleGrad(atoms, check=True)¶
Partial derivatives of bond angle restraints re: each coordinate.
- Parameters:
atoms (Atoms) – coordinates for current (trial) structure.
check (bool) – cross-check vs. finite differences (takes longer).
- Returns:
partial derivatives of angle residuals: ∂R/∂x where R is the sum of penalties for restrained bond angles.
- Return type:
ndarray[N, 3]
- Author:
Davis Catolico (pseudo-code attempt, superseded by MSC)
- Author:
Michael S. Chapman (rewritten)
- Author:
Brynmor K. Chapman (finds commutation error)
Warning
This all needs very careful checking. It is not clear that the derivation was every proof-checked by Michael in its LaTeX typset form. It appears that the code from Davis contained syntax errors, suggesting that it was never tested or run.
For a least squares restraint:
(1)¶
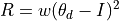
where
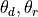 are the actual bond angles in degrees,
radians; I is the ideal value; and the weight
are the actual bond angles in degrees,
radians; I is the ideal value; and the weight
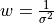 is related to the estimated error,
is related to the estimated error,
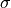 .
.(2)¶
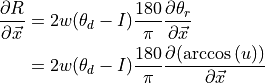
(3)¶
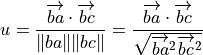
where
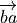 is the vector from atom b to a,
and
is the vector from atom b to a,
and 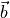 signifies
signifies 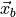 .
.(4)¶
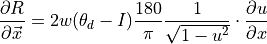
(5)¶
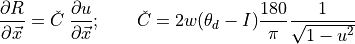
where
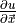 depends on the positions
depends on the positions
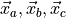 of atoms a, b, c, and where
of atoms a, b, c, and where
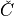 is an invariant term common to all the positional partial
derivatives.
The derivative
is an invariant term common to all the positional partial
derivatives.
The derivative 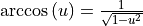 is taken from eqn. 31,
CRC derivatives A-62.
is taken from eqn. 31,
CRC derivatives A-62.(6)¶
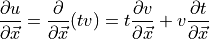
(from CRC manual A-60 Derivatives eqn. 5), where
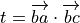 and
and ![v = \left[\| ba \|^2 \| bc \|^2\right]^{-1/2}](_images/math/0f5123a1fc0799594b9876ecdad9e3af690c2925.png)
noting that
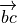 does not depend on
does not depend on 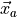 :
:(7)¶
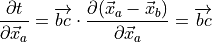
(8)¶
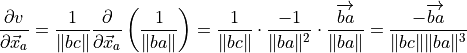
(9)¶
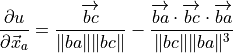
Alternatively,
(10)¶
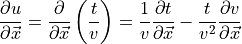
(from CRC manual A-60 Derivatives eqn. 7), where
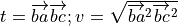 .
.Noting that
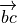 is independent of
is independent of 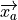 ,
and can be taken outside the derivative, and that as
,
and can be taken outside the derivative, and that as
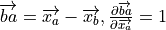 :
:(11)¶
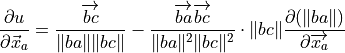
(12)¶
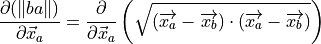
(13)¶
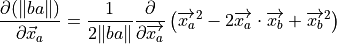
(14)¶
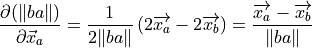
(15)¶
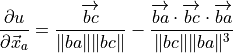
By symmetry:
(16)¶
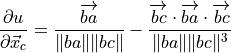
As the angle is invariant with overall translation, one can infer:
(17)¶
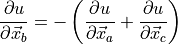
- angleGrad_dc(atoms, check=True)¶
Partial derivatives of bond angle restraints re: each coordinate.
Code author: Davis Catolico
Deprecated since version 0.5.6: Michael’s updated version is angleGrad(), but not yet tested.
- angleResidual(atoms, verbose=False)¶
Objective function for Covalent bond angles
- Parameters:
atoms (Atoms) – current (trial) coordinates
- Returns:
- Return type:
float
- angleStats(atoms, verbose=False)¶
RMSDs for Covalent bond angles
- Parameters:
atoms (Atoms) – current (trial) coordinates
- Returns:
number of restrained bonds, weighted RMSD, unweighted RMSD
- Return type:
float, float
- angle_sigma = 1.0¶
Default estimated standard deviation for bond angles not in dictionary.
- f(atoms)¶
Objective function for Covalent bonding restraint
- Parameters:
atoms (Atoms) – current (trial) coordinates
- Returns:
weighted sum of length, angle, dihedral residual terms
- Return type:
float
- f_grad(atoms)¶
Partial derivatives of Covalent bonding restraint re: position, occupancy
- Parameters:
atoms (Atoms) – coordinates for current (trial) structure.
- Returns:
- Return type:
(ndarray[N, 3],)
Todo
add occupancy into tuple
- get_history()¶
get the history for f and f_grad
- length¶
- Variables:
~.length (list(tuple)) – i_atom_A, i_atom_B, target, sigma
~.angle (list(tuple)) – i_atom_A, i_atom_B, i_atom_C, target, sigma
- lengthDeviants(atoms, threshold=3.0)¶
Deviations from ideal of covalent bond lengths above threshold*esd.
- Parameters:
atoms (Atoms) – current (trial) coordinates
threshold (float) – eg. 3.0 to print deviations >= 3 sigma.
- Returns:
Table of greatest deviations
- Return type:
str
- lengthGrad(atoms, check=False)¶
Partial derivatives of bond length restraints re: each coordinate.
- Parameters:
atoms (Atoms) – coordinates for current (trial) structure.
check (bool) – cross-check vs. finite differences (takes longer).
- Returns:
Σj|isin|N ∂P/∂xi, where P is the bond length penalty, for pairs of N atoms with coordinates x. P = (|xi - xj| - L)2 = (D - L)2, where L is the ideal length, so: ∂P/∂xi = 2(D - L) ∂P/∂xi = 2((D-L)/D)(xi - xj), and similarly: ∂P/∂xj = -2((D-L)/D)(xi - xj)
- Return type:
ndarray[N, 3]
Todo
Add partial derivative re: occupancy, and multiply x partials by o; suggest using the minimal occupancy of the two atoms.
- lengthResidual(atoms, verbose=False)¶
Objective function for Covalent bond lengths
The conventional least-square restraint on distance gives a gradient/residual ratio that is much higher than for density-fitting. Might want to experiment with a “softer” function.
- Parameters:
atoms (Atoms) – current (trial) coordinates
- Returns:
P = Σ{W(||xi - xj| - Lideal|)}, where W is the inverse variance of the ideal length.
- Return type:
float
- lengthStats(atoms, verbose=False)¶
RMSDs for Covalent bond lengths
- Parameters:
atoms (Atoms) – current (trial) coordinates
- Returns:
number of restrained bonds, weighted RMSD, unweighted RMSD
- Return type:
float, float
- length_sigma = 0.01¶
Default estimated standard deviation for bond lengths not in dictionary.
- torsionGrad(atoms, check=True)¶
Partial derivatives of torsion angle sterochemical restraints re: each coordinate.
Documentation needs to be proofed:…
(18)¶
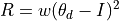
where
 is the torsion angle (degrees), I is the ideal
target and
is the torsion angle (degrees), I is the ideal
target and 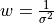 is a weight based on the
error,
is a weight based on the
error, 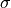 .
.For atoms a, b, c, d, the dihedral,
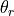 rad,
around bc is given by:
rad,
around bc is given by:(19)¶
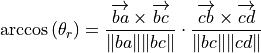
No this is wrong …
- Parameters:
atoms (Atoms) – coordinates for current (trial) structure.
check (bool) – cross-check vs. finite differences (takes longer).
- Returns:
partial derivatives of torsion angle residuals: ∂R/∂x where R is the sum of penalties for restrained bond angles.
- Return type:
ndarray[N, 3]
- Author:
Michael S. Chapman (rewritten)
- update(hist, value)¶
update the history
- Parameters:
hist (str) – ‘f’ or ‘f_grad’ designating the history to extend
value (str) – text
- class restraints.Distance_id(index, atoms, equivalent=[0, 0], symmetry=None, minimum=None, maximum=None, weight=1.0, parent=None)¶
Bases:
objectSpecific pair of atoms between which there is a distance restraint
Distance restraint
- Parameters:
index ([int,int]) – indices of the two atoms
atoms (Atoms) – coordinates to which index refers
equivalent ([int,int]) – indices of symmetry operators applied to atoms before distance calculation; 0 for unit operator
symmetry (Symmetry) – object containing the operators
minimum (float) – minimum distance (Angstrom)
maximum (float) – maximum distance (Angstrom)
weight (float) – applied to residual component
parent (Distance_id|NoneType) – Distance_id from which this is being generated by symmetry or re-ordering, if applicable.
- childless()¶
Childless version of self.
- deviation(atoms)¶
Current deviation of this pair-wise distance beyond limits.
Negative if less than minimum.
- Parameters:
atoms (Atoms) – coordinate set
- Returns:
deviation (Angstrom)
- Return type:
float
- deviation_str(atoms)¶
Documenting discrepancy of structure with restraint.
- Parameters:
atoms (Atoms) – coordinate set
- Returns:
distance and deviation from maximum (if positive), minimum (if negative)
- Return type:
str
- distance(atoms)¶
Current distance between the atoms.
- Parameters:
atoms (Atoms) – coordinate set
- Returns:
distance (Angstrom)
- Return type:
float
- family()¶
Iterator over self & parent.
- partial(atoms, check=False, asymmetric_only=False)¶
Partial derivatives of a distance restraint re: each coordinate.
Let G be a component of a distance deviation residual: G = wD2, where:
deviation, D = L - T; L = ((Qa - Rb)2)1/2 - T
a, b are (column) position vectors of atoms in the asymmetric unit
Q, R are (4,4) augmented symmetry operators to transform to positions, separated by distance, L, and where T is the target distance for a least-squares restraint with weight, w.
∂G/∂a = 2wD∂D/∂a;
∂D/∂a = ((Qa - Rb)/L)Q;
So, by chain rule ∂G/∂a= 2wD((Qa - Rb)/L)Q;
Similarly, ∂G/∂b= -2wD((Qa - Rb)/L)R;
- Parameters:
atoms (Atoms) – coordinates for current (trial) structure.
check (bool) – cross-check vs. finite differences (takes longer).
asymmetric_only (bool) – non-zero only for atoms that are within the asymmetric unit, and not symmetry-expanded. This will be compatible with residuals calculated so as not to double count distances that bridge between symmetry-equivalents.
- Returns:
∂G/∂xi, non-zero for x = a|b
- Return type:
ndarray[N, 3]
Todo
Add partial derivative re: occupancy, and multiply x partials by o; suggest using the minimal occupancy of the two atoms.
- residual(atoms)¶
Atom-pair’s contribution to a weighted least-squares residual
The residual is halved if an atom is a symmetry equivalent and weighted by the atoms’ occupancy. Thus, cross-links between symmetry equivalents and alternate conformers are not double-counted.
- Parameters:
atoms (Atoms) – coordinate set
- Returns:
weighted squared deviation * fraction of atoms in asymmetric unit
- Return type:
float
- vector(atoms)¶
Vector from atoms[self.index[0]] to atoms[self.index[1]].
- Parameters:
atoms (Atoms) – coordinate set
- Returns:
column vector
- Return type:
ndarray((3,1))
- class restraints.Distance_input(*seq, **named)¶
Bases:
dictParsed input for a distance restraint command (maximum and/or minumum).
- class restraints.Distance_selection(distance, atoms)¶
Bases:
objectDistance restraint as atoms.Selections
Warning
Need to check that this can be instantiated after symmetry-expansion.
Convert dictionary input of user text into atoms.Selections
- Parameters:
~.distance (Distance_input(dict)) – from str selection, to str selection, min, max, weight
atoms (Atoms) – atomic structure, already symmetry-expanded
Todo
If can’t count on atoms being symmetry-expanded, will need the ability to update self.whither and self.whence when symmetry- equivalents (or atoms therin) are added.
- deviation(atomsFr, atomsTo, intramolecular=False, intermolecular=False)¶
Smallest deviation of |atomsFr[:,self.whither]-atomsTo[:,self.whence]| outside min, max limits
If no atom-pair falls within the distance limits, returns information on the pair closest to satisfying the limits: (deviation, indices, [[]]). If pair(s) fall(s) with the limits, then returned is (0.0, None, indices-array), where the array points to pairs of atoms that satisfy the limits.
The deviation is in Angstrom and negative if distance < min; positive if distance > max; 0 if within limits.
If none of the self.whence atoms satisfy the inter- or intra-molecular criterion than None is returned.
- Parameters:
atomsFr (Atoms) – structure
atomsTo (Atoms) – either atomsFr or its symmetry transformation
intramolecular (bool) – consider only distances between atoms in same chain
intermolecular (bool) – consider only distances between atoms in different chains
- Returns:
(deviation, index-pair|None, pair-indices)|None
- Return type:
(float, tuple|NoneType, ndarray(shape=(:,2))|NoneType
Todo
Consider short-cut, stopping when found a pair within limits, but note that then would not fully document all pairs.
- deviation1(xyz, atoms, which=None)¶
Smallest deviation of |atoms[…,which&whither]-xyz| outside min, max limits
If no atom currently falls within the distance limits, returns information on the atom closest to satisfying the limits: (deviation, index, []). If atom(s) fall(s) with the limits, then returned is (0.0, None, index-array), where the array points to the atoms that satisfy the limits.
The deviation is in Angstrom and negative if distance < min; positive if distance > max; 0 if within limits.
If no atoms are in the Selection which & self.whither, returns None.
- Parameters:
xyz (ndarray) – single atom position
atoms (Atoms) – structure
which (Selection) – which atoms to consider; default is self.whence
- Returns:
(deviation, atom_index|None, atom-indices)|None
- Return type:
(float, int|NoneType, ndarray)|NoneType
- deviation_sym(atoms, symmetry=None, intramolecular=False, intermolecular=False, fixWhence=False)¶
Between atom selections (or sym equivs), smallest deviation outside min, max limits
If no atom-pair falls within the distance limits, returns information on the pair closest to satisfying the limits: (deviation, indices, equivalents, [[]], [[]]). If pair(s) fall(s) with the limits, then returned is (0.0, None, None, indices-array, equivalents-array), where the arrays refer to pairs of atoms that satisfy the limits. Equivalents are the symmetry operations for the atoms that satisfy or come closest to satisfying the limits. 0 is used for the unit operator. Indices point to atoms in the original protomer from which the distance pair could be regenerated by application of the numbered symmetry operator. Only the local (molecular) operators from symmetry are considered, not any space group or crystal lattice operations.
The deviation is in Angstrom and negative if distance < min; positive if distance > max; 0 if within limits.
- Parameters:
atoms (Atoms) – structure
symmetry (Symmetry) – definition of the symmetry operations
fixWhence (bool) – symmetry transform only the self.whither atoms; else the self.whence atoms as well
intramolecular (bool) – consider only distances between atoms in same chain
intermolecular (bool) – consider only distances between atoms in different chains
- Returns:
(deviation, index-pair|None, pair-indices)
- Return type:
(float, tuple|NoneType, tuple|NoneType, ndarray(shape=(:,2), ndarray(shape=(:,2))
- Raises:
ValueError – if no atoms pairs satisfy input criteria
Todo
Consider short-cut, stopping when found a pair within limits, but note that then would not fully document all pairs.
- class restraints.Distances(atoms, symmetry=None)¶
Bases:
objectRestraints for minimal and maximal distances, suitable for x-linking.
Restraints are defined by add() which searches through selected atoms, and their symmetry equivalents, looking for pairs that satisfy the minimum and maximum limits. If none, the pair that is closest is identified, and it is this deviation that contributes to the refinement residual.
Warning
These atom identifications are currently not updated. This will avoid discontinuities in gradient and function evaluation, for smooth refinement, but will not impose restraints if a previously satisfied restraint is violated, and will not switch to a new atom pair if another becomes closest.
Todo
An update() method that will re-evaluate the atom pairings, and a with_update option to calculate(). Test to see if the discontinuities can be tolerated.
Initialize restraints for ancillary distances (eg. cross-links).
- Parameters:
atoms (Atoms) – structure
symmetry (Symmetry) – object with which to generate equivalents
- add(from_all, to_any, intramolecular=False, intermolecular=False, minimum=None, maximum=None, weight=1.0)¶
Add a distance restraint
- Parameters:
from_all (str) – to be parsed into a Selection of atoms, all of which are subject to the restraint
to_any (str) – to be parsed into a Selection to atoms, any one of which is to be used as the restraint target for each atom in from_all
intramolecular (bool) – consider only distances between atoms in same chain
intermolecular (bool) – consider only distances between atoms in different chains
minimum (float) – distance in Angstrom
maximum (float) – distance in Angstrom
weight (float) – for harmonic flat-well distance potential
- calculate(atoms, verbose=False)¶
Calculate residual & partial derivatives with respect to coordinates
Iterates over distances that have been input, and their symmetry equivalents, summing the least-squares residual and its partial partial derivatives for atoms in the asymmetric unit.
Partials are returned as a tuple for future support of occupancy partials.
- Parameters:
atoms (Atoms) – coordinate set
verbose (bool) – print statistics
- Returns:
residual, partials
- Return type:
float, (ndarray(shape=(3,N)),)
Todo
Support for occupancy refinement with return of dbydocc.
- doc¶
Documentation of how each restaint was generated
- entry¶
List of objects specifiying either a distance restraint or pairs of atoms that already satisfy it
- class restraints.Geometry¶
Bases:
objectSuperclass for definition/retreival of residue’s ideal stereochemistry.
- angle(*atoms, **opts)¶
Restraint for a bond angle at the middle atom.
The middle atom should in in the residue-type defined by the sub-class.
- Parameters:
*atoms (str) – three atom names
prior (str) – residue type of 1st atom if different from 2nd.
next (str) – residue type of 2nd atom if different from 2nd.
- bond(*atoms, **opts)¶
Restraint for a bond length.
- Parameters:
*atoms (str) – two atom names
linked (str) – 2nd residue type if atoms bridge 2 residues.
- Returns:
ideal value, estimated error (Angstrom)
- Return type:
float, float
- Raises:
KeyError – if not found
- class restraints.PairIDs(atom_indices, atoms, which_operators=None, symmetry=None)¶
Bases:
objectMatched arrays of indices for atom pairs and their symmetry operators.
Store arrays of index-pairs/operators and list the corresponding operator names.
- Parameters:
atom_indices (ndarray((N,2))) – pairs of indices for Atoms coordinates.
atoms (Atoms) – coordinates
which_operators (ndarray((N,2))) – operator indices for each of the indexed atoms.
symmetry (Symmetry) – object storing the symmetry operators / names.
- class restraints.RestraintsSubCommands(parent, prompt='sub-command')¶
Bases:
SubCmdSub-commands for supplementary restraints.
- Parameters:
parent (
TopCmdinstance) – Cmd object whence this call was made, usually self.prompt (str) – concatonated with the parent’s prompt.
- ap2 = ArgumentParser(prog='sphinx-build', usage=None, description='SELECTION_1 [AND] SELECTION_2', formatter_class=<class 'argparse.HelpFormatter'>, conflict_handler='error', add_help=True)¶
- do_distance(args)¶
Add a distance (cross-linking) restraint.
- do_information(arg=None, opts=None)¶
Report statistics on ancillary restraints.
- class restraints.Tasks¶
Bases:
objectHolder of restraints task methods to be subclassed by other programs.
Superclass for restraints-related common tasks.
Warning
If this class defines pre-requisites on which other tasks depend, then this superclass must be instantiated before the other tasks are defined. If this class depends on pre-requisites defined elsewhere, then it must be instantiated afterwards. It may not be possible to satisfy both requirements!
- restraints(information=False)¶
Set up / report ancillary restraints (B-factor, distance).
- Parameters:
information (bool) – report statistics only, then quit.
- Returns:
rms deviations (B-factors, distances).
- Return type:
tuple of float(s)|NoneType
- restraints_distance(*args, **kwargs)¶
Add a distance (cross-linking) restraint.
- restraints_distance_prereq(*args, **kwargs)¶
Pass-through, trying to meet the prerequisites.
- restraints_information(verbose=True)¶
Report ancillary restraints (B-factor, distance).
- Parameters:
verbose (bool) – information on individual distance restraints.
- Returns:
rms deviations (B-factors, distances).
- Return type:
tuple of float(s)|NoneType
- restraints_information_prereq(*args, **kwargs)¶
Pass-through, trying to meet the prerequisites.
- restraints_prereq(**kwargs)¶
Pass-through, trying to meet the prerequisites.
- class restraints.VDWRestraint(atoms, weight=1, parameterization=None, symmetry=None, max_shift=1.0, radiiPath=None, exclude_ss=True, same_conformer=True, conformer_coupling=0.0)¶
Bases:
objectRestraint on overlapping van der Waal radii of atoms
Excludes all pairs of SG atoms on basis that might be disulfide.
Changed in version Reimplemented: to reduce incapacitating memory usage. Previously stored several (natom, natom) float matrices, and now stores only boolean matrices designating which interactions to recalculate, now every time. Nearly 100x faster.
Warning
Does not support “open” symmetry, only closed symmetry in which repeated application of the same operator returns you to the starting point. Algorithms use efficiencies of closed symmetry in searching for potential contacts. Closed symmetry includes all crystal symmetry and most molecular symmetry, but not all non-crystallographic symmetry.
Warning
applies the full restraint to atoms with partial occupancies, ignoring the possibility that in multi-conformer structures, conformers might be selected in mutually compatible (non-overlapping) ways.
Todo
account for open symmetry
Todo
account for states that are only sometimes occupied
- Parameters:
atoms (Atoms) – coordinates (used to extract atom types etc., but positions will be updated for each restraint calculation).
weight (float) – multiplier for the vdW residual restraint.
parameterization (:py:class:'AtomicParameterization' or sub-class) – definition of what parameters are refining and how they depend on atomic parameters. This is used here to limit calculation of vdW overlap & partials to those that will affect moving atoms.
symmetry (Symmetry/NoneType) – defines molecular & lattice symmetry, if any.
radiiPath (str) – file name for a python dictionary to extend or over-ride default vdW radii.
max_shift (float) – maximum expected change in atomic coordinates, used in pre-calculating possible contacts.
exclude_ss (bool) – exclude contacts between pairs of SG atoms on the assumption that they are CYS residues and, if close, they are likely disulfide-bridged.
same_conformer (bool) – overlap is only considered between atoms from the same conformer (A, B, …) or if one of the pair is single- conformer (no letter).
conformer_coupling (float) – NOT IMPLEMENTED YET… if 1.0, minimal overlap will be calculated, assuming that alternate conformers (where present) completely resolve any overlap. This could be a reasonable approximation if “common atom” models and pseudo-symmetry in rotamers were considered (neither currently supported). If conformer_coupling=0.0, conformer selections are assumed to be uncoupled (random) and therefore the restraint is multiplied by the product of the two atoms’ occupancies. Both are approximations, coupled likely to underestimate vdW overlap and uncoupled likely to overestimate. Intermediate values 0.0 < conformer_coupling < 1.0 will lead to a weighted sum of the two approaches. Note that inappropriate (un)coupling could lead to over- or under- estimation of the conformational diversity if their occupancies are being refined.
- Variables:
~.distance – cut-off used to determine from the initial structure which atom pairs might get close enough for van der Waals repulsion. This distance is also used as the cut-off for the generation of symmetry equivalents, unless the equivalents have already been generated with a larger cut-off.
- ..warning:: If the degree of coupling is not appropriately approximated,
then refinement of conformer occupancies can be biased by over- or under-estimating the degree of real van der Waals overlap. Should consider whether really need to use the restraint when refining conformer occupancies.
- ..warning:: Currently considering refinement of the occupancies of
rotamers generated on the fly, but this class will only consider positions explicitly defined in the atomic coordinates.
Todo
Exclude contacts from different PDB-defined conformers.
Todo
Exclude contacts w/in same residue, assuming that they will be handled by stereochemical constraints / restraints.
Todo
Handling of hydrogens. The default radii assume that hydrogens are explicitly defined, but most (low resolution) structures do not include them.
- class Status(parent, atoms)¶
Bases:
objectStatus of vdW contacts.
- Parameters:
parent (VDWRestraint) – self of the owning class
atoms (Atoms) – current coordinates
- connectivityExclusion = 3¶
Atoms connected by this or fewer bonds will be excluded from the restraint.
E.g. if atoms a, b, c, d are bonded: a–b–c–d, then all pair except a … d will be excluded.
In other’s refinements, torsion angles would be restrained explicitly, not through vdW (connectivityExclusion = 3), and even without torsional restraints a value of 3 might be needed to avoid locking dihedrals to exactly staggered conformations. With a value of 2, expect dihedrals to be regularized.
- distance = 5¶
Neighbors within at least distance will used in vdW calculations.
The actual distance might be larger, if symmetry-equivalent neighbors have previously been calculated with a larger distance.
- f(atoms)¶
Objective function for VDW restraint
- Parameters:
atoms (Atoms) – current (trial) coordinates
- Returns:
V = w Σi|isin|N Σj|isin|N {(|xi - xj| - (ri + rj)}p, where V is the van der Waals penalty summed over pairs of N atoms with positions x and radii, r, and where p is self.power and w is the product of self.weight and self.weightFactor
- Return type:
float
Todo
Multiply by the occupancies for simplest approach
Todo
Multiply by sum of occupancies - 1, assuming fully coordinated conformers/rotamers with the simplification that the other conformers do not have atoms that form the same vdW contacts.
- f_grad(atoms)¶
Partial derivatives of vdW restraint re: each coordinate.
- Parameters:
atoms (Atoms) – coordinates for current (trial) structure.
- Returns:
Σj|isin|N ∂V/∂xi, where V is the van der Waals penalty, for pairs of N atoms with coordinates x.
- Return type:
(ndarray[N, 3],)
Warning
Does not properly account for open symmetry. Does not work with open symmetry because it ignores certain interactions. If atoms a and b, and their symmetry equivalents a’ and b’, were arranged:
a --- b b'--- a'
Then motion of a in the y direction would affect the residual of b in a way not taken into account here. Fixing this would greatly increase the computational cost.
Todo
Multiply by the occupancies for simplest approach
Todo
Multiply by sum of occupancies - 1, assuming fully coordinated conformers/rotamers with the simplification that the other conformers do not have atoms that form the same vdW contacts.
Todo
Add partial derivative re: occupancy, and multiply x partials by o. QQQ Returning as a tuple, so that dfbydocc can be added.
- get_history()¶
get the history for f and f_grad
- get_neighbors(atoms, cache=True)¶
Get the neighbors, using the symmetry module.
- Parameters:
atoms (Atoms) – Unique set of coordinates.
cache (bool) – try using cached neighbor matrix & radii if change < self.max_shift (always updating the coordinates)
- Returns:
symmetry-expanded coordinates, their vdW radii, boolean matrix of which are potentially close
- Return type:
Atoms, ndarray, ndarray
Todo
options to exclude same residue, conformer
- static matrix_bonded(bonds, bondsExcluded=0)¶
calculate higher degree of bonding connectedness and returns it in matrix form
- Parameters:
bonds (list) – the bonds lists
bondsExcluded (int) – atom pairs separated by < = bondsExcluded bonds be excluded.
- Returns:
matrix with 1 if atoms within bondsExcluded, else 0.
- Return type:
numpy.matrix(shape = (n, n), dtype = int)
- power = 2¶
Pauli exclusion repels overlapping atoms with force = k.r^11.
This would be too harsh for smooth optimization, so a softer exponent (2) should be used - entirely empirical.
- radius = {'AS': 2.0, 'BR': 1.95, 'C': 1.7, 'CL': 1.8, 'CU': 1.4, 'F': 1.35, 'H': 1.2, 'I': 2.15, 'N': 1.5, 'O': 1.4, 'P': 1.9, 'S': 1.8, 'SB': 1.85, 'SE': 2.0, 'TE': 2.2}¶
Default vdW radii.
radiiPath is a hook to enable this to be user over-ridden or extended. However, radiiPath is not yet available as an input argument.
Atoms that are not listed will be given a default radius of 1.5 A.
- status(atoms)¶
van der Waals statistics.
- Parameters:
atoms (Atoms) – coordinates.
- Returns:
object containing number and rms of overlaps, as well as list of worst infractions.
- Return type:
- update(hist, value)¶
update the history
- Parameters:
hist (str) – ‘f’ or ‘f_grad’ designating the history to extend
value (str) – text
- weightFactor = 50¶
The restraint weight is internally scaled by this, in addition to the user-entered weight. (Avoids user-entered weights being numerically large.)
- restraints.distance_arg_parse(*arg)¶
Grab 2 atom selections from arg.
- Parameters:
arg (list(str)) – command arguments
kwargs (dict) – command options
- Return dict restraint_entry:
Distance_input dictionary
- restraints.ss(atoms, verbose=False)¶
Identify pairs of Cys sulfur atoms.
- Parameters:
atoms (Atoms) – coordinates
- Returns:
A_i,j is True when i & j are both SG atoms
- Return type:
ndarray(shape=(natom, natom), dtype=bool)